Perform complement-dependent cytotoxicity assay
- Ability to monitor complement-dependent cytotoxicity
- Capture images of stained target cells before and after complement killing
- Provide direct cell counts for measuring percent cytotoxicity
Calcein AM release assay to measure complement-dependent cytotoxicity
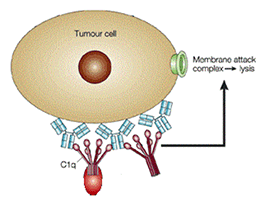
In order for the complement cascade to be activated, the circulating complement protein C1q must first be recruited to the cell surface by the bound immunoglobulins on the tumor cell surface. The initiation of the complement cascade leads to the downstream formation of the membrane attack complex. The membrane attack complex forms a pore on the cell surface and thereby permeabilizes the cell membrane which leads to cell death.

(Adapted from) Paul Carter. (2001) Improving the efficacy of antibody-based cancer therapies. Nature Reviews Cancer 1:11, 118-129
By staining the target tumor cells with cytoplasmic dye Calcein AM, we can monitor cell death by examining the retention of Calcein AM within the cell. Only live tumor cells with intact cell membranes will retain the green dye while the dead cells will release the Calcein into the surrounding media. Based on the retention of the dye the Celigo™ image cytometer software can enumerate the number of live target tumor cells over time.
Measure CDC (complement dependent cytotoxicity) using direct cell counting of Calcein AM stained target cells
Celigo experimental protocol
- Target cells (adherent or suspension) were collected and stained with Calcein AM
- Target cells were seeded in the wells of microplates
- Complements were added to the wells
- Antibodies were added to the wells at different concentrations
- The wells were scanned and analyzed using the Celigo for direct cell counting of Calcein AM stained target cells
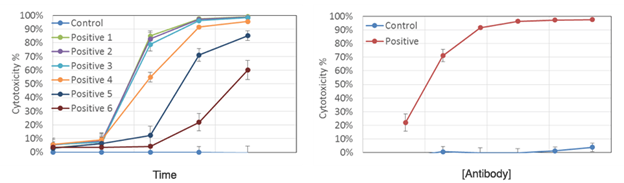
- By observing the reduction in target cell number over time we can determine the percent cytotoxicity for the complement dependent cytotoxicity assay.
Dose-dependent CDC images
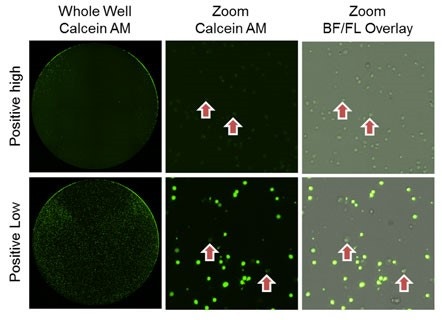
As time and antibody concentration increased, the number of Calcein AM stained target cells decreased
Low [antibody], lower cytotoxicity is shown
High [antibody], high cytotoxicity in shown, where almost 100% of the cells lost the Calcein AM fluorescence
CDC time-dependent dose response results
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























