Benefits of using celigo for cell cycle analysis
- Perform different cell cycle experiments using a single platform
- Analyze cell cycle data using built-in gating interface
- No need to trypsinize adherent cells to perform cell cycle assay
Introduction
Cell cycle analysis is often used for the screening of compounds that affect cell growth and proliferation. The Celigo image cytometer allows users to conduct cell cycle analysis on adherent cells using assays typically developed for flow cytometry. The flexible gating interface of the Celigo software is used to identify and quantify populations of cells in each phase of the cell cycle. This analysis can be conducted using a single dye such as DAPI or using a second marker for DNA synthesis such as a BrdU stain. It has the potential to be multiplexed with a marker for mitosis such as histone H3 phosphorylation.
Cell cycle PI
Protocol
- Seed A375 cells in a 96-well plate
- Treat with selected drugs or vehicle control
- Fix in ice cold 100% Methanol for 15 minutes
- Stain with cell cycle PI reagent for 40 minutes
- Image entire 96-well plate (whole well imaging) in ~15 minutes
- Analyze cell cycle data using Celigo gating interface ~ 20 minutes
Results: Cell cycle assay using A375 Cells with staurosporine-treated positive control

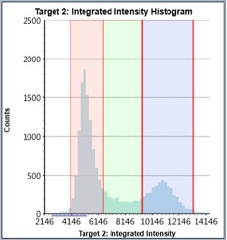
Control – Histogram
Counted PI+ cells at different cell cycle stages
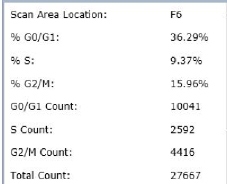
Results
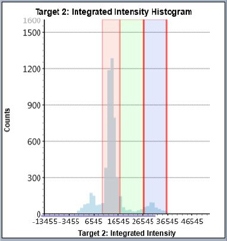
Staurosporine-Treated – Histogram
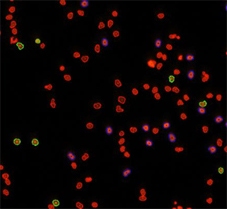
Counted PI+ cells at different cell cycle stages
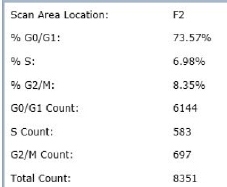
Results
Cell cycle EdU/DAPI
Protocol
- Seed A549 cells in a 96-well plate
- Treat with selected drugs or vehicle control
- Add media with EdU per well
- Fix in ice cold 100% Methanol for 15 minutes
- Stain with DAPI
- Image entire 96-well plate (whole well imaging) in ~15 minutes
- Analyze cell cycle data using Celigo gating interface ~ 20 minutes
Results: Cell cycle assay using A375 cells with staurosporine-treated positive control
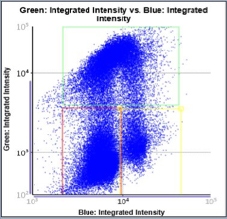
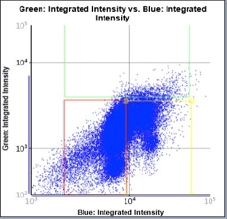
Control – Scatter Plot
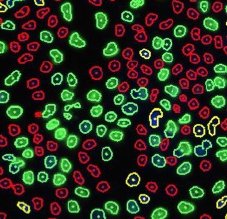
Identified EdU and DAPI stained cells different cell cycle stages
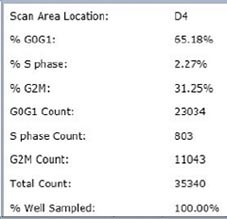
Results
Treated – Scatter Plot
Identified EdU and DAPI stained cells different cell cycle stages
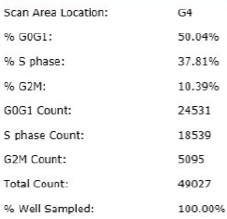
Results
Cell cycle BrdU/DAPI
Protocol
- Seed 8000-10000 cells/well in 96-well plate in a final volume of 100 μl/well.
- Incubate cells overnight at 5% CO2, 37 °C.
- Drug compound treatment
- BrdU incorporation
- Fixation and DNA denaturation
- Antibody Labeling to detect BrdU
- Nuclear Stain with DAPI
- Image entire 96-well plate (whole well imaging) in ~15 minutes
- Analyze cell cycle data using Celigo gating interface ~ 20 minutes
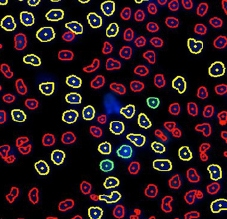
Typical images and nuclear identification should look as follow:
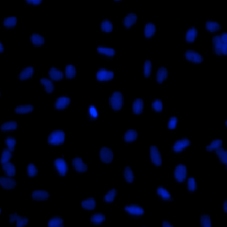
DAPI cell image
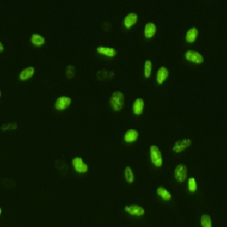
BrdU cell image
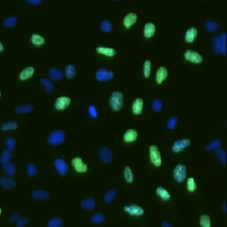
DAPI and BrdU cell image
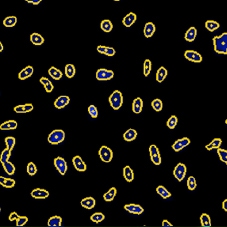
DAPI mask segmentation
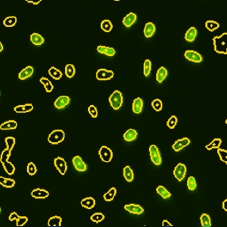
BrdU mask segmentation

DAPI and BrdU mask segmentation
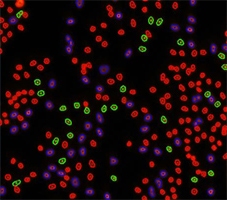
Step 1. Place the 3 gates as follows and cells will be color-identified on the image:
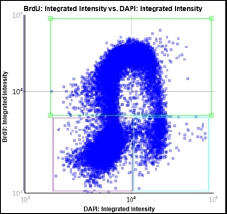
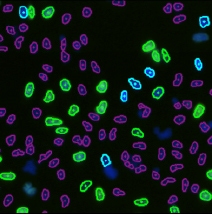
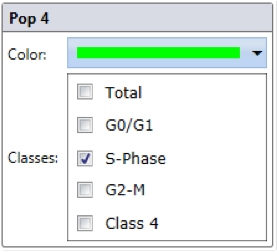
Step 2. Assign each gated population of cells to the correct class as follow. The color of the gate will match the color of the population of cells and the segmentation outlines on the image.

Step 3. Select wells to analyze and “Start Analyze”
Step 4. The data is organized according to the plate map for each of the G0/G1, S- and G2/M class of cells.
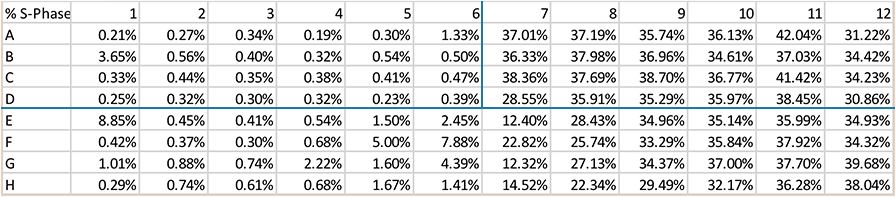
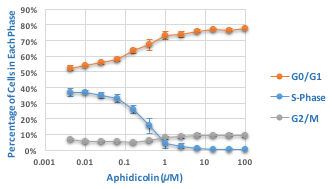
Effect of aphidicolin on cell cycle
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























