Detect and monitor viability of 3D tumor spheroids
- Directly image tumor spheroids in various microwell formats
- Non-invasive brightfield imaging allows the user to image the same plate over multiple days
- Perform a two-color fluorescent viability assay
Introduction
The Celigo image cytometer has been developed to fully automate imaging and analysis of tumorspheres. This automated morphometric analysis tool significantly reduces the time and effort needed to quantify key aspects of 3D spheres including size, growth, growth tracking over time and response to chemotherapeutics.
Monitor viability of 3D tumor spheroids

Experimental setup
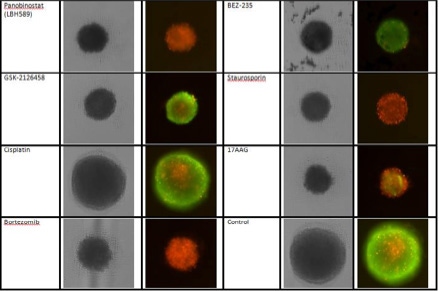
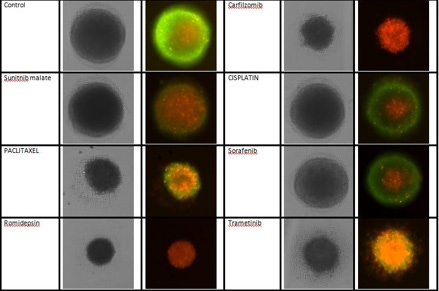
3D cultures were treated with multiple drugs (17-AAG, Paclitaxel, TMZ or Doxorubicin) and stained for viability after 21 days.
Live / dead stains used were Calcein AM (green), Propidium Iodide (red) to measure live and dead cells on days 4, 7, 10, 14, and 17. Plates containing spheroids were imaged on Celigo image cytometer.
- 17-AAG decreased sphere size and caused the most significant cell death
- Paclitaxel decreased sphere size but maintained a significant number of live cells
- Temozolomide caused no significant decrease in sphere size and did not cause cell death
- Doxorubicin decreased sphere size and caused significant cell death
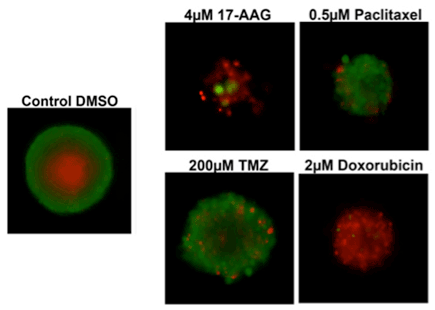
Multi-drug viability 3D assay
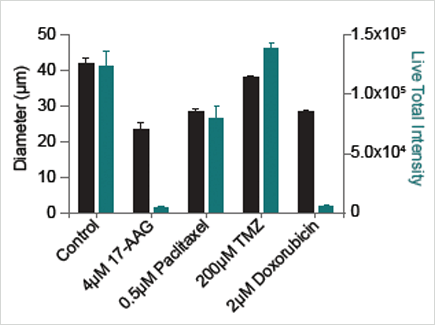
Spheroid diameter (black) and total live fluorescent intensity (green) after drug treatment.
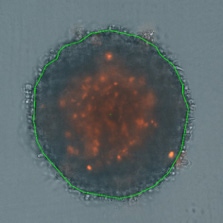
3D tumor spheroids treated at different drug concentrations and stained with propidium iodide
Control
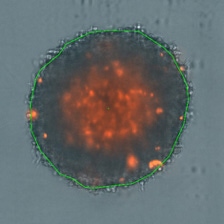
Medium drug dose
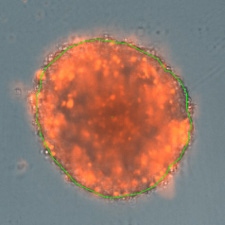
High drug dose
Measuring viability 3D spheroids with morphological differences
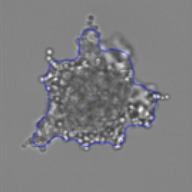
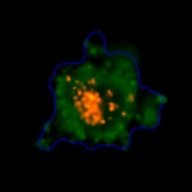
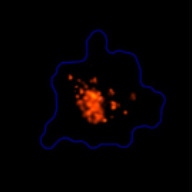
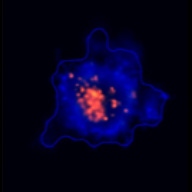
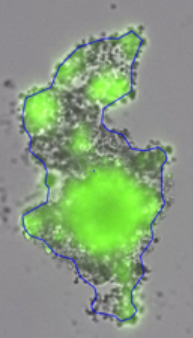
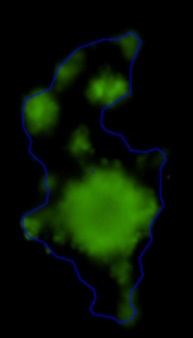
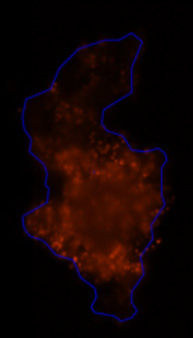
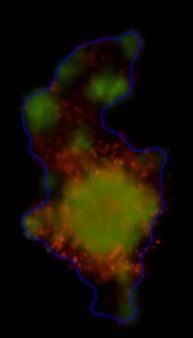
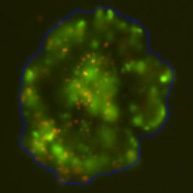
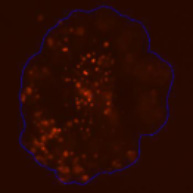

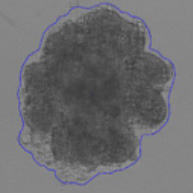
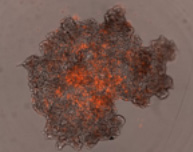
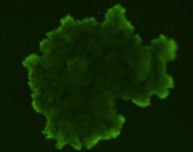
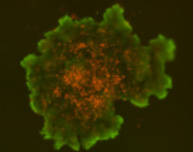
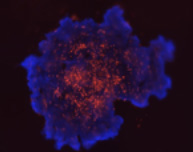
3D tumor spheroids treated with various compounds and stained with calcein-AM and PI
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























